
This observation tells us that accounting statements are important in investment and credit decisions, but they are not the sole source of information for making investment and credit decisions. The accounting equation states that total assets is equal to total liabilities plus capital. This lesson presented the basic accounting equation and how david raissipour senior vice president engineering and products carbonite it stays equal. If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation. The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
It is sometimes called net assets, because it is equivalent to assets minus liabilities for a particular business. ” The answer to this question depends on the legal form of the entity; examples of entity types include sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. A sole proprietorship is a business owned by one person, and its equity would typically consist of a single owner’s capital account. Conversely, a partnership is a business owned by more than one person, with its equity consisting of a separate capital account for each partner. Finally, a corporation is a very common entity form, with its ownership interest being represented by divisible units of ownership called shares of stock.
What Is a Liability in the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity). To make the Accounting Equation topic even easier to understand, we created a collection of premium materials called AccountingCoach PRO. Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more. When a company purchases goods or services from other companies on credit, a payable is recorded to show that the company promises to pay the other companies for their assets. There are different categories of business assets including long-term assets, capital assets, investments and tangible assets. They were acquired by borrowing money from lenders, receiving cash from owners and shareholders or offering goods or services.
Arrangement #2: Net Value = Assets – Liabilities
Cash (asset) will reduce by $10 due to Anushka using the cash belonging to the business to pay for her own personal expense. As this is not really an expense of the business, Anushka is effectively being paid amounts owed to her as the owner of the business (drawings). The cash (asset) of the business will increase by $5,000 as will the amount representing the investment from Anushka as the owner of the business (capital). Incorrect classification of an expense does not affect the accounting equation.
What Are the Three Elements in the Accounting Equation Formula?
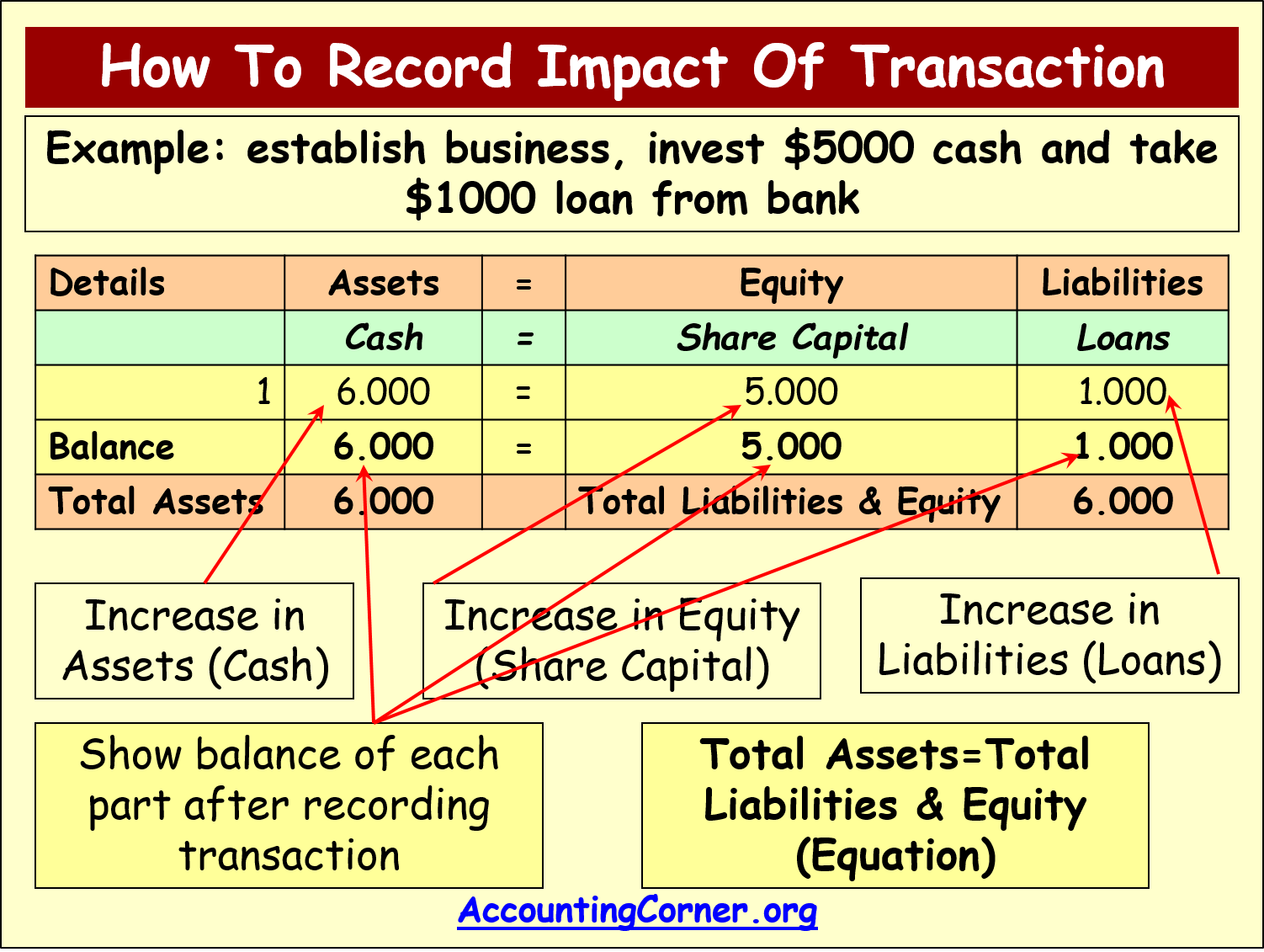
Every transaction alters the company’s Assets, Liabilities and Equity. It’s the accountants’ responsibilities to keep an accurate journal of these transactions. Every transaction’s impact to Assets must have either offsetting impact to Assets or matching impact to Liabilities and Equity. It’s called the Accounting Equation because it sets the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The system is the go-to accounting method of the modern day.
Thus, the accounting equation is an essential step in determining company profitability. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. Our Explanation of Accounting Equation (or bookkeeping equation) illustrates how the double-entry system keeps the accounting equation in balance.
The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. Our Accounting Equation Cheat Sheet provides eight transactions to illustrate why and how the accounting equation remains in balance. The value of your house after paying down mortgage belongs to you.
- Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation.
- The Accounting Equation states that the total value of a company’s Assets must equal the total value of its Liabilities and Equity.
- Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their “real” value, or what they would be worth on the secondary market.
Due within the year, current liabilities on a balance sheet include accounts payable, wages or payroll payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are usually owed to lending institutions and include notes payable and possibly unearned revenue. Accountants and members of a company’s financial team are the primary users of the accounting equation. Understanding how to use the formula is a crucial skill for accountants because it’s a quick way to check the accuracy of transaction records . Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
For example, if a company buys a $1,000 piece of equipment on credit, that $1,000 is an increase in liabilities (the company must pay it back) but also an increase in assets. The basic formula of accounting equation formula is assets equal to liabilities plus owner’s equity. As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets.
The main limitation of the Accounting Equation is that it doesn’t tell us anything about the company. The formula is more of a principle than a metric that yields significant insight. Said differently, it states whatever value of Assets left after covering Liabilities is entitled to Equity holders. It doesn’t tell us anything unique about any specific business. It doesn’t tell us how the business is performing, whether its financial health, or how much the company is worth.
As a result of the transaction, an asset in the form of merchandise increases, leading to an increase in the total assets. At this point, let’s consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business. Like any brand new business, it has no assets, liabilities, or equity at the start, which means that its accounting equation will have zero on both sides.
Leave a Reply